The Suez Canal is one of the most crucial waterways in international shipping, playing a vital role in global trade by providing a direct maritime route between Europe and Asia. Here’s an in-depth look at its importance:
Strategic Location
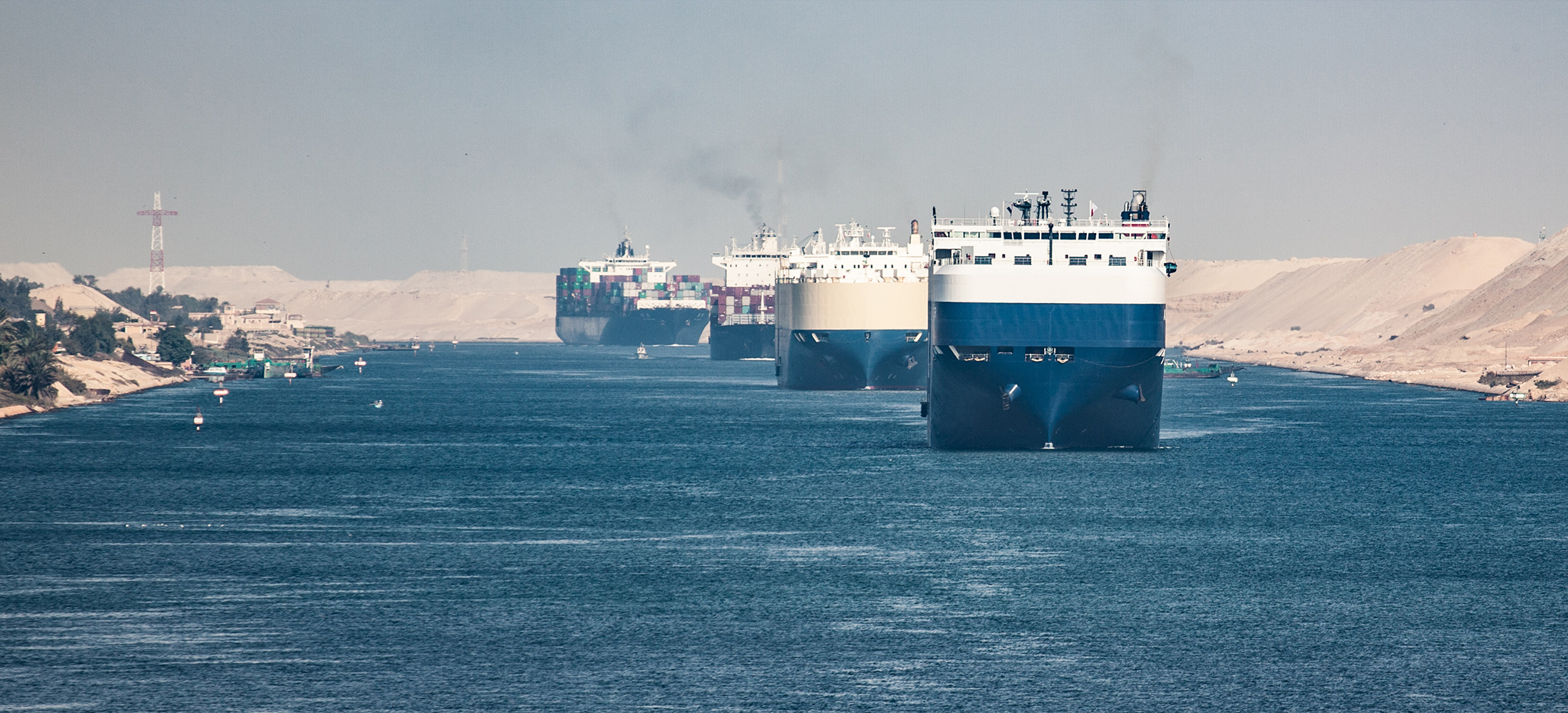
The Suez Canal connects the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, facilitating a direct shipping route between Europe and Asia. This strategic location significantly reduces travel time and distance for ships, bypassing the need to navigate around the southern tip of Africa via the Cape of Good Hope.
The canal serves as a critical link in one of the world’s busiest trade routes, handling approximately 12% of global trade. It is particularly essential for the transportation of oil, liquefied natural gas (LNG), and containerized goods.
Time and Cost Efficiency
By providing a shortcut between Europe and Asia, the Suez Canal cuts the sea voyage by about 7,000 kilometers (approximately 4,300 miles), significantly reducing transit times. For example, a journey from the Persian Gulf to Europe via the Suez Canal is roughly half the distance compared to the route around Africa.
Shorter routes result in lower fuel consumption and reduced operating costs for shipping companies. These cost savings are crucial for the competitiveness of global trade, allowing goods to be transported more efficiently and at lower prices.
Economic Significance
The Suez Canal is a major source of revenue for Egypt, generating billions of dollars annually through tolls paid by transiting vessels. This income is vital for the Egyptian economy, supporting infrastructure development and other national projects.
Any disruptions in the Suez Canal can have significant repercussions on global markets. Delays or blockages can lead to increased shipping costs, supply chain disruptions, and higher prices for goods worldwide, underscoring the canal’s importance to international commerce.
Capacity and Infrastructure
The Suez Canal Authority has undertaken several expansion projects to accommodate the growing size and volume of global shipping traffic. The most notable project, completed in 2015, involved the construction of a new parallel channel and the widening and deepening of existing sections, allowing for the simultaneous passage of ships and reducing transit times.
The canal is capable of accommodating some of the largest container ships and tankers in operation today. This capacity is crucial for the efficient movement of high-volume cargo, supporting the demands of global trade.
Strategic and Geopolitical Importance
A significant portion of the world’s energy supplies, including oil and LNG, passes through the Suez Canal. The canal’s role in the global energy market is critical, as it facilitates the reliable and efficient transportation of energy resources from the Middle East to Europe and beyond.
The Suez Canal’s strategic importance gives Egypt significant geopolitical leverage. Control over such a vital waterway influences regional and global politics, making it a focal point for international maritime strategy.
Historical Significance
Completed in 1869, the Suez Canal is considered one of the greatest engineering feats of the 19th century. Its construction revolutionised global trade by drastically reducing the travel distance between Europe and Asia.
The canal has been the site of several historic events, including conflicts and blockades that have highlighted its strategic importance. These events have shaped international policies and underscored the need for maintaining open and secure maritime routes.
Environmental Considerations
The Suez Canal has also had ecological impacts, including the introduction of invasive species between the Red Sea and the Mediterranean. Managing these environmental effects is an ongoing challenge for the canal’s administration and surrounding regions.
Efforts are being made to enhance the canal’s environmental sustainability, including initiatives to reduce carbon emissions from ships and improve waste management practices within the canal zone.
Ever Given Incident:
In March 2021, the grounding of the Ever Given, a massive container ship, blocked the Suez Canal for six days. This incident highlighted the canal’s critical role in global trade, as the blockage disrupted supply chains and caused significant economic losses worldwide.
2015 Expansion:
The completion of the Suez Canal expansion project in 2015 increased its capacity and allowed for greater efficiency in handling maritime traffic. This expansion has reinforced the canal’s status as a vital artery for international shipping.
The Suez Canal’s importance in international shipping cannot be overstated. Its strategic location, capacity to handle large vessels, and role in reducing transit times and costs make it indispensable for global trade. As a key economic asset for Egypt and a critical component of global supply chains, the Suez Canal will continue to be a focal point for international commerce and geopolitics.
If you would like to discuss this further please contact us to arrange a consultation with one of our experts.